This is the current affairs of 30 & 31 January 2026. Here are questions and answers of daily current affairs for better preparation of competitive exams for government jobs.
PDF Download: Click here
1. According to the Economic Survey 2025–26, what is the estimated GDP growth rate for the financial year 2026–27?
a. 2.1% to 3.2%
b. 4.5% to 5.1%
c. 5.2% to 6.9%
d. 6.8% to 7.2%
Answer: d. 6.8% to 7.2%
Economic Survey 2025–26
– Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Economic Survey 2025–26 in both Houses of Parliament.
– It has been prepared under the leadership of Chief Economic Adviser V. Anantha Nageswaran.
– It is presented in Parliament every year before the Budget.

GDP growth rate estimated at 6.8% to 7.2% in 2026–27
– The Economic Survey estimates the GDP growth rate for FY 2026–27 to be between 6.8% and 7.2%.
– The GVA (Gross Value Added) growth rate is estimated at 7.3%.
– It emphasizes cautious optimism amid global uncertainty.
————–
2. According to the Economic Survey 2025–26, which country did India overtake to become the world’s fourth-largest economy with a GDP value of $4.18 trillion?
a. Japan
b. Germany
c. France
d. China
Answer: a. Japan
India’s GDP value at $4.18 trillion
– With a gross domestic product (GDP) of $4.18 trillion, India has overtaken Japan to become the world’s fourth-largest economy.
– In the next 2.5 to 3 years, it is expected to displace Germany from third place, with India’s GDP projected to reach $7.3 trillion by 2030.
– The Government of India’s capital expenditure has increased from ₹2.63 lakh crore in FY 2018 to ₹11.21 lakh crore in FY 2026 (BE), reflecting nearly a 4.2-fold increase.
– In FY 2025–26, the Centre’s revenue receipts reached 9.2% of GDP.
– This confirms India’s fiscal discipline, with an estimated achievement of the 4.4% fiscal deficit target through public investment and consolidation.
————–
3. According to the Economic Survey 2025–26, what was the total value of India’s exports in the financial year 2024–25?
a. $525.3 billion
b. $625.3 billion
c. $825.3 billion
d. $925.3 billion
Answer: c. $825.3 billion (Goods sector: $437.7 billion and Services sector: $387.6 billion)
India’s total exports reach a record $825.3 billion
– Between 2005 and 2024, India’s share in global merchandise exports nearly doubled from 1% to 1.8%.
– India’s total exports reached a record $825.3 billion in FY 2024–25, registering a 6.1% increase over the previous year, mainly driven by strong growth in services exports.
– In FY 2024–25, services exports reached $387.6 billion with a growth of 13.6%, an all-time high.
Largest recipient of remittances
– India remains the world’s largest recipient of remittances.
– In FY 2024–25, remittance inflows reached $135.4 billion.
Increase in foreign exchange reserves
– India’s foreign exchange reserves rose to $701.4 billion as of January 16, 2026, sufficient to cover 11 months of imports and 94% of external debt.
India’s foodgrain production
– Foodgrain production of rice, wheat, maize, and coarse cereals has increased.
– Due to good monsoon rainfall, India’s foodgrain production in agricultural year 2024–25 is estimated to reach 3577.3 lakh metric tonnes (LMT).
– This is 254.3 lakh metric tonnes higher than the previous year.
– According to the Economic Survey, this increase is due to higher production of rice, wheat, maize, and coarse cereals (Shri Anna).
—————
4. According to the Economic Survey 2025–26, by what percentage did the problem of obesity increase among children under 5 years of age in India (in 2019–21)?
a. 2.1%
b. 2.9%
c. 3.4%
d. 5.1%
Answer: c. 3.4%
What does the data indicate?
– The survey cites National Family Health Survey (NFHS) data showing that 24% of Indian women and 23% of men are overweight or obese.
– In 2015–16, 2.1% of children under five years of age were overweight.
– By 2019–21, this figure increased to 3.4%.
– This indicates a rising problem of obesity/overweight among young children.
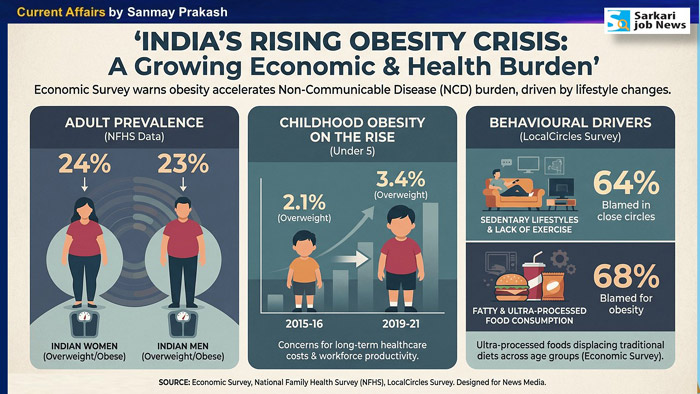
Why is it termed “More troubling still”?
– Traditionally, discussions in India have focused on undernutrition, low weight, and stunting, but now the issue of overnutrition is also emerging.
– India is facing a “double burden of malnutrition”: undernourished children on one hand and overweight children on the other.
What are the social and health implications?
– Poor dietary habits
– Junk food consumption
– Lack of physical activity
– Urbanization and lifestyle changes
Obesity emerging as a threat for India
– Obesity among children under five is becoming a new public health challenge alongside undernutrition.
– Concern has been expressed over the rising consumption of ultra-processed foods high in fat, salt, and sugar, making India one of the fastest-growing markets for such products.
– The Economic Survey has advocated restrictions on advertising of such products from morning till late night.
– It has also suggested restrictions on the marketing of milk and beverages for infants and young children.
————–
5. Other important facts from the Economic Survey 2025–26
Advantage of late entry into AI
– The chapter “Evolution of the AI Ecosystem in India” states that India’s relatively late entry into Artificial Intelligence is a hidden but major advantage.
– According to the survey, countries that adopted AI very early adopted models that are highly energy-intensive, extremely expensive, and financially risky.
– Because India entered the AI sector later, it can avoid these mistakes and develop low-energy, low-cost, and more sustainable AI models.
– AI is expected to impact 10–20% of jobs.
——
– Under PMJDY (Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana), 55.02 crore bank accounts had been opened by March 2025, of which 36.63 crore are in rural and semi-urban areas.
– By September 2025, the number of unique investors is expected to cross 12 crore, of which about 25% will be women.
– During April–December 2025, domestic inflation averaged 1.7%.
– In FY 2025–26, private final consumption expenditure grew by 7%, reaching 61.5% of GDP, the highest level since 2012 (the same share was also recorded in FY 2023).
– In agricultural year 2024–25, India’s foodgrain production is estimated to reach 3577.3 lakh metric tonnes (LMT), 254.3 LMT higher than the previous year. Note: The agricultural year is considered from 1 July to 30 June of the following year.
– Since the launch of the PM-Kisan scheme, more than ₹4.09 lakh crore has been disbursed to eligible farmers.
– Manufacturing GVA grew by 7.72% and 9.13% in the first and second quarters of FY 2025–26 respectively, indicating structural recovery.
– Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes across 14 sectors have attracted actual investments of over ₹20 lakh crore, resulting in additional production/sales of over ₹187 lakh crore and creation of more than 126 lakh jobs by September 2025.
– Under the India Semiconductor Mission, 10 projects involving investments of around ₹1.60 lakh crore are included.
– High-speed railway corridors increased nearly tenfold: from 550 km in FY14 to 5,364 km by FY26 (December 2025); 3,500 km of railway lines were added in FY26.
– India is the world’s third-largest domestic aviation market, with the number of airports increasing from 74 in 2014 to 164 in 2025.
– A historic turnaround for DISCOMs (electric distribution companies): for the first time, a positive profit of ₹2,701 crore was recorded in FY 2025.
– India ranks third globally in renewable energy and installed solar capacity.
– India became the fourth country to achieve autonomous satellite docking (SPaDeX) capability. SPaDeX refers to two satellites docking in space autonomously without human control.
– Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) at primary, upper primary, and secondary levels is 90.9, 90.3, and 78.7 respectively.
– In times of global uncertainty, Atmanirbhar Bharat is essential.
Government debt
– The central government achieved its fiscal deficit reduction target ahead of schedule.
– In FY 2025, the fiscal deficit stood at 4.8% of GDP, while the target for FY 2026 is 4.4%.
– Fiscal deficit refers to the excess of government expenditure over its income; a lower deficit indicates a stronger economy and lower inflation.
Rising debt of states
– The Economic Survey 2025–26 identifies rising state debt and weak fiscal discipline as a major fiscal risk.
– According to the survey, several large states have increased spending on expenditure schemes, particularly populist welfare schemes, leading to higher revenue deficits and increased market borrowing.
– As a result, some states had to borrow even for day-to-day expenses, increasing their debt-to-GDP ratios and putting pressure on financial stability.
– The survey suggests that states should maintain fiscal discipline by controlling expenditure, enhancing revenue, and focusing on long-term investments to contain debt risks.
————–
6. From which two states/UTs were two new species of rare ant flies, ‘Metadon ghorpadei’ and ‘Metadon reimeri’, discovered?
a. Kerala and Tamil Nadu
b. Tamil Nadu and Delhi
c. Kerala and Delhi
d. Telangana and Tamil Nadu
Answer: b. Tamil Nadu and Delhi
– The discovery was made by H. Shankararaman, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore, and S. S. Anuj, Assistant Professor, College of Agriculture, Vellayani, under Kerala Agricultural University.
– One ant fly was found in a disturbed urban forest in Delhi and the other in the Western Ghats of Tamil Nadu, highlighting the importance of conserving both urban green spaces and biodiversity hotspots.
– The species are named Metadon ghorpadei and Metadon reimeri.
– The larvae of these flies live inside ant nests and feed on ant larvae.
– This special behavior is called myrmecophily, making them extremely rare and difficult to identify.
– So far, only six species of the Metadon genus have been reported from India.
– Of the 454 species recorded worldwide, only 27 are found in the Indian subcontinent.
—————
7. In which tiger reserve of Madhya Pradesh was the endangered species Dhole dog spotted?
a. Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve
b. Panna Tiger Reserve
c. Kanha Tiger Reserve
d. Ratapani Tiger Reserve
Answer: d. Ratapani Tiger Reserve
– The endangered Dhole dog was sighted in Ratapani Tiger Reserve near Bhopal on January 22, 2026.
– Its photograph was shared on January 23 via the official social media handle of Ratapani Tiger Reserve.
– According to tiger reserve officials, this is a very positive sign from an ecological perspective.
– It will not only enhance biodiversity but also promote domestic and international tourism in Bhopal.
– This is the sixth wildlife species captured on camera so far in 2026.
Dholes are known for stealing prey from tigers
– Dhole is a species of Asian wild dog.
– It is reddish-brown in color, agile, and highly social.
– It lives in packs of 14 to 20.
– It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
– It preys on large ungulates such as deer and sambar.
– Sometimes, it even steals prey from tigers or bears.
198 bird species recorded
– A recent bird census in Ratapani Tiger Reserve recorded 198 bird species.
– In the January 2022 census, 150 species were recorded.
————–
8. Which state has announced that it will celebrate 2026 as the ‘Year of Agriculture’?
a. Gujarat
b. Rajasthan
c. Uttar Pradesh
d. Madhya Pradesh
Answer: d. Madhya Pradesh
– Governor Mangubhai Patel announced on January 26, 2026, that 2026 will be celebrated as the ‘Year of Agriculture’.
– Keeping in mind the vision of “Prosperous Farmer – Prosperous State,” the government has prepared a ten-point model for agricultural development.
– This includes the use of technology, measures to increase income, promotion of natural farming, export facilitation, innovation, and digital transparency, which will soon be implemented across the state.
Efforts to boost milk production
– The government is working on special schemes to make Madhya Pradesh the “Milk Capital” of the country.
– The per-animal subsidy in gaushalas for destitute cattle has been increased from ₹20 to ₹40.
– The budget has also been increased from ₹250 crore to ₹505 crore.
————–
9. When is Shaheed Diwas observed?
a. 25 January
b. 30 January
c. 23 March
d. b and c
Answer: d. b and c (30 January and 23 March)
– Shaheed Diwas is observed on 30 January in memory of Mahatma Gandhi.
– On this day in 1948, Nathuram Godse assassinated Mahatma Gandhi by shooting him.
– On 23 March 1931, revolutionaries Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev, and Rajguru were hanged by the British.
————–
10. Indian player Ilyas Pasha passed away on January 22, 2026. Which sport was he associated with?
a. Football
b. Cricket
c. Tennis
d. Badminton
Answer: a. Football
– Former India and East Bengal defender, 61-year-old footballer Ilyas Pasha, passed away after a prolonged illness.
– Pasha was considered one of Karnataka’s finest footballers.
– The All India Football Federation (AIFF) expressed condolences on his demise.
– He began his football career with Vinayaka Football Club.
– His hard work and playing skills took him to the Indian Telephone Industries (ITI) club in the mid-1980s.
– He made his India debut against Bulgaria in the Nehru Cup on January 27, 1987, in Kozhikode.
– He played eight international matches, including two Nehru Cups (1987 and 1991), the 1991 SAF Games, and the 1992 Asian Cup qualifiers.
– He won two Santosh Trophy titles with Bengal in 1993 and 1995.
– He was part of the 1990 Triple Crown–winning East Bengal team.
– He was also part of the team that won the club’s first international trophy, the Wai Wai Cup, in 1993.




