This is the current affairs of 15 & 16 January 2026. Here are questions and answers of daily current affairs for better preparation of competitive exams for government jobs.
PDF Download: Click here
1. Which space agency carried out the first-ever mission in history to bring a sick astronaut back to Earth from the International Space Station (ISS) for emergency medical treatment?
a. ESA
b. Roscosmos
c. NASA
d. JAXA
Answer: c. NASA
{Although the crew included astronauts from JAXA and Roscosmos as well, it was not disclosed who exactly fell ill}
– In January 2026, a piece of news came from the ISS (International Space Station) that shocked the entire world.
– For the first time, NASA was forced to abandon its mission midway.
– A sick astronaut was brought back to Earth through emergency medical evacuation.
– This is the first medical rescue mission in NASA’s history.
– The astronaut was brought back using SpaceX’s spacecraft.

What happened in space?
– During the Crew-11 mission, one astronaut’s health suddenly deteriorated. The situation was so serious that—
– The mission had to be immediately cut short.
– A decision was taken to return one month earlier than scheduled.
– The entire crew had to leave the ISS and return.
– After spending five months in space, the mission had to be terminated midway due to health issues. The American space agency has refused to share any details about the health problem but has emphasized that the return was not an emergency situation.
What did NASA say?
– NASA admitted that the case was “serious but stable,” but the risk was high enough that treatment in space was not possible.
Emergency landing in the dead of night
– SpaceX’s Crew Dragon Endeavour capsule made a nighttime splashdown directly into the Pacific Ocean near California.
– A medical team standing by transported the astronaut directly to a hospital by helicopter. All of this happened within minutes.
Who were part of the Crew-11 mission?
– Zena Cardman (NASA)
– Mike Fincke (NASA)
– Kimiya Yui (Japan – JAXA)
– Oleg Platonov (Russia – Roscosmos)
Who fell ill?
– NASA has kept secret which astronaut fell ill and what the illness was.
– The reason given was medical privacy, but this silence has raised more questions.
Why is this case so significant?
– For the first time, an ISS mission was halted solely for medical reasons and an astronaut was brought back to Earth in an emergency.
– NASA had to admit that not every situation in space can be controlled.
– Experts believe that long-duration space missions pose major risks to the human body. Microgravity, radiation, and isolation can break the body down internally.
What now on the ISS?
– The number of crew members on the ISS has been reduced.
– Three other members are still present on the operational ISS.
– No spacewalks will be conducted for the next few days due to reduced crew strength.
– The next mission may be sent earlier in 2026.
ISS operations only till 2030
– The International Space Station (ISS) will be deliberately de-orbited around 2030 and its remains will be guided to a safe area in the ocean.
– The ISS was built in 1998, meaning by 2030 it will be over 30 years old.
– Operating a structure in space for such a long time becomes risky and expensive.
– Its original design life was around 15–20 years. Over time, structural and technical challenges have been increasing.
—————-
2. What is India’s ranking in the Henley Passport Index 2026 (released in January)?
a. 80th
b. 70th
c. 82nd
d. 84th
Answer: a. 80th
– According to the Henley Passport Index 2026 (released in January), India’s ranking is 80.
– India shares the 80th rank jointly with Algeria and Niger.
– Indian passport holders get visa-free entry to 55 countries.
– India’s ranking is better than the October 2025 report.
– The Henley Passport Index is released multiple times a year.

India’s position in the Henley Passport Index
– January 2026: 80th rank
– October 2025: 85th rank
– July 2025: 77th rank
– January 2025: 85th rank
Ranking of neighboring countries
– Afghanistan: 101
– Pakistan: 98
– Nepal: 96
– Bangladesh: 95
– Sri Lanka: 93
– Myanmar: 89
– China: 59
Visa-free countries for Indians
– Angola, Barbados, Bhutan, British Virgin Islands, Burundi, Cambodia, Cape Verde Islands, Comoros Islands, Cook Islands, Djibouti, Dominica, Ethiopia, Fiji, Grenada, Guinea-Bissau, Haiti, Indonesia, Jamaica, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kiribati, Laos, Macau (China), Madagascar, Malaysia, Maldives, Marshall Islands, Mauritius, Micronesia, Mongolia, Montserrat, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nepal, Niue, Palau Islands, Philippines, Qatar, Rwanda, Samoa, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Sri Lanka, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Tanzania, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, and Zimbabwe.
Henley Passport Index
– It is a global ranking that measures the strength of passports by showing how many countries can be entered without a visa or with visa-on-arrival.
– The ranking is prepared by London-based firm Henley & Partners using data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
—————-
3. According to the Henley Passport Index 2026 (released in January), which country secured the top spot in the list of the world’s most powerful passports?
a. Italy
b. Singapore
c. France
d. USA
Answer: b. Singapore
– The top three passports in the index are from Asian countries.
– Singapore’s passport also topped the list in 2024 and 2025.
– Holders of Singapore passports can enter 192 out of 227 countries and territories visa-free.
– Note: The USA is ranked 10th. Its citizens can travel visa-free to 179 countries.
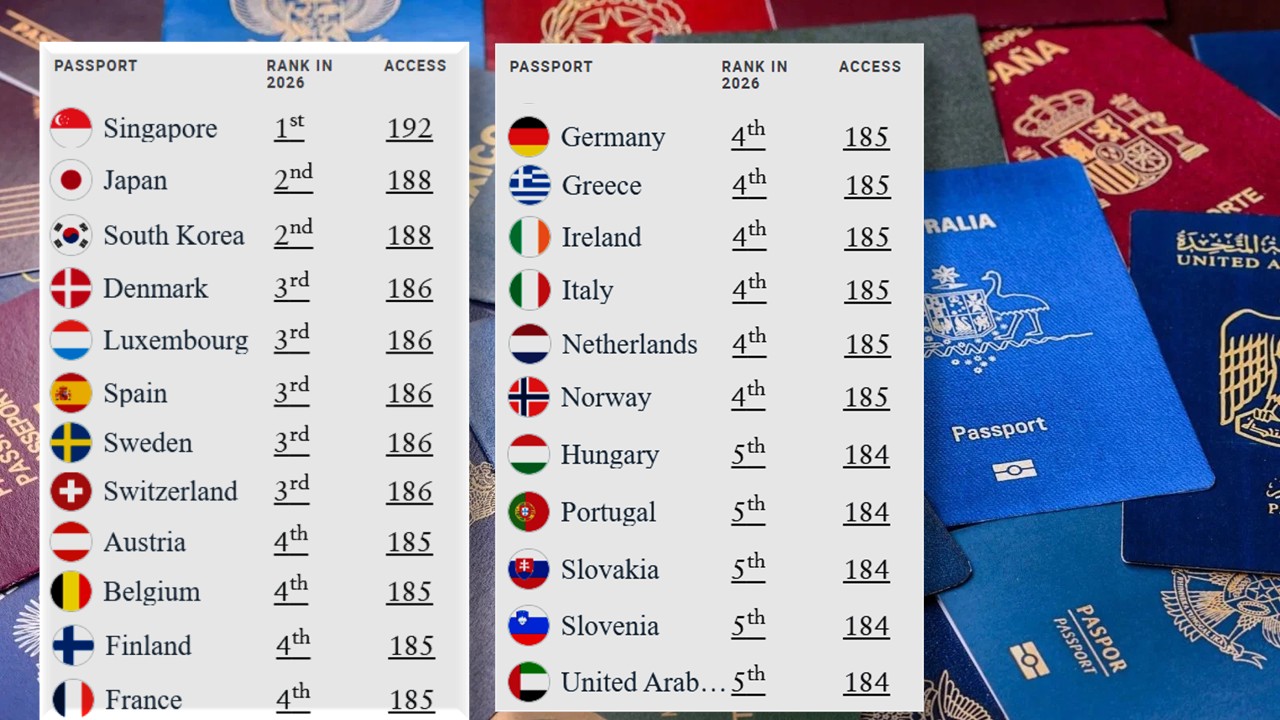
Top 5 Rank
Rank 1: Singapore (Visa-free entry to 192 countries)
Rank 2: Japan, South Korea (Visa-free entry to 188 countries)
Rank 3: Denmark, Luxembourg, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland (Visa-free entry to 186 countries)
Rank 4: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Netherlands, Norway (Visa-free entry to 185 countries)
Rank 5: Hungary, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, UAE (Visa-free entry to 184 countries)
Worst rankings
– Rank 101: Afghanistan
– Rank 100: Syria
– Rank 99: Iraq
– Rank 98: Pakistan, Yemen
– Rank 97: Somalia
– Rank 96: Nepal
————–
4. Who has the central government appointed as the new Director General (DG) of the Border Security Force (BSF)?
a. Praveen Kumar
b. Vijay Meena
c. Ajay Kumar
d. Nirlosh Kumar
Answer: a. Praveen Kumar
– The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet took this decision in January 2026.
– Praveen Kumar is a 1993-batch IPS officer of the West Bengal cadre.
– Earlier, he was serving as DG of ITBP and was holding additional charge of BSF.
————–
5. Who has the central government appointed as the new Director General (DG) of the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)?
a. Veer Pratap Singh
b. Shatrujit Singh Kapur
c. Vijay Singh Rana
d. Dubesh Kumar
Answer: b. Shatrujit Singh Kapur
– The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet took this decision in January 2026.
– Shatrujit Singh Kapur is a 1990-batch IPS officer of the Haryana cadre.
– He will remain in office till October 31, 2026, i.e., his date of retirement, or until further orders.
—————
6. Who has the central government appointed as the new Director General (DG) of the National Investigation Agency (NIA)?
a. Vivek Agarwal
b. Rakesh Ahuja
c. Vinod Prakash
d. Rakesh Agarwal
Answer: d. Rakesh Agarwal
– The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet has appointed the in-charge DG of NIA as the permanent DG.
– He was serving as the Special Director General of NIA.
– He will remain in office till July 31, 2028, or until further orders.
– He is a 1994-batch IPS officer of the Himachal Pradesh cadre.
—————-
7. What was the retail inflation rate in December 2025?
a. 1.25%
b. 1.33%
c. 0.71%
d. 0.25%
Answer: b. 1.33%
– Retail inflation (CPI) in India rose by 1.33% in December 2025, compared to 0.71% in November 2025.
– December’s retail inflation rate is the highest in the last three months, though it remains well below the RBI’s lower comfort level of 2%.
– The RBI’s inflation target is 4%, with a tolerance band of ±2%.
– Who releases the retail inflation data?
NSO (National Statistical Office)
– Under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation
– How is retail inflation determined?
– It is based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
– It includes inflation in food items, fruits, clothing, footwear, housing, fuel, electricity, and others.
– CPI measures the average price paid by consumers for goods and services in the retail market.
How does inflation affect us?
– Inflation directly affects purchasing power. For example, if inflation is 6%, the value of ₹100 earned becomes only ₹94.
– Therefore, investments should be planned keeping inflation in mind, otherwise the value of money decreases.
How does RBI control inflation?
– To control inflation, liquidity in the market is reduced.
– For this, RBI increases or decreases the repo rate.
– When inflation rises, RBI increases the repo rate; when inflation becomes very low, it reduces the repo rate.
– Recently, inflation has been under control, which is why RBI did not change the repo rate for the ninth consecutive time in August.
Inflation limits set by RBI
– RBI’s inflation target is 4% based on CPI, with a permissible range of ±2%.
– Thus, inflation below 2% or above 6% is not considered healthy for economic growth.
————–
8. What was the wholesale inflation rate in December 2025?
a. 0.83%
b. (-) 0.32%
c. (-) 1.21%
d. (-) 2.21%
Answer: a. 0.83%
– Wholesale inflation (WPI) in India stood at 0.83% in December 2025, up from (-) 0.32% in November 2025.
– The Ministry of Industry said the main reason was a month-on-month increase in prices of food articles, non-food items, and manufactured products.
Who releases the wholesale inflation data?
– Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT)
– Under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry
(Note: Retail inflation data is released by NSO.)
What is wholesale inflation?
– It is based on the Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
– WPI reflects prices charged by one business to another in the wholesale market.
– These prices are related to bulk business transactions.
(Note: Retail inflation is based on CPI.)
—————
9. Where did the Home Minister lay the foundation stone for India’s first state-funded BSL-4 (Bio-Safety Level-4) laboratory?
a. Gandhinagar (Gujarat)
b. Ahmedabad (Gujarat)
c. Mumbai (Maharashtra)
d. Noida (Uttar Pradesh)
Answer: a. Gandhinagar (Gujarat)
– Union Home Minister Amit Shah laid the foundation stone of the BSL-4 containment lab in Gandhinagar on January 15, 2026.
– This facility will be India’s first state-government-funded BSL-4 lab capable of researching the most dangerous category of microorganisms.
– Gujarat’s BSL-4 lab will strengthen India’s biosecurity and mark a major step in scientific research, pandemic response, and health sciences.
– It will also prepare India to combat future pandemics.
– This will be the second civilian BSL-4 lab in India (the first is at NIV, Pune), but the first state-funded facility.
– However, at the end of 2024, DRDO under the Ministry of Defence established its own BSL-4 lab in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
What is a BSL-4 lab?
– BSL-4 is the highest level of bio-safety.
– Research is conducted on highly dangerous and infectious viruses for which no definitive treatment or vaccine exists, such as Ebola, Marburg, Nipah, and Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever (CCHF).
– Cost: ₹362 crore
– Standards: Developed as per international safety guidelines
– Management: Under Gujarat Biotechnology Research Centre (GBRC)
– National facility: Recognized as a National Centre for High Containment under central bio-policy
– The facility will include BSL-4, BSL-3, BSL-2, ABSL-4, and ABSL-3 lab modules with advanced facilities and supporting infrastructure.
Why is this lab important?
– Dangerous virus samples will no longer need to be sent far away, speeding up diagnosis.
– Preparedness for future pandemics: Post-COVID-19, the importance of high-containment labs is clear.
– Strategic asset for the state and the country.
– Help in studying zoonotic diseases (animal-to-human transmission).
– Provides a global platform for young scientists and researchers.
– Contributes to the development of vaccines, medicines, and disease-control technologies.
—————
10. Which country did India surpass to become the world’s largest rice producer in 2024–25?
a. USA
b. China
c. Brazil
d. Australia
Answer: b. China
– India has now become the world’s largest rice producer, surpassing China.
– In 2024–25, India produced around 150 million metric tonnes of rice, while China produced about 145.28 million metric tonnes.
– India’s share in global rice production is now around 28%.
Why did rice production increase?
– Rice cultivation in India has grown rapidly over the past decade, with production nearly quadrupling and cultivated area expanding.
– Due to farmers and schemes like MSP, rice has remained an attractive option.
– Major increases have been seen in states like Punjab, Haryana, and Chhattisgarh.
Continuous growth in production
Year – Area suitable for all seasons – Production (in million tonnes)
1969–70: 37.67 million hectares – 40.43 million tonnes
1979–80: 39.42 million hectares – 42.33 million tonnes
1989–90: 42.16 million hectares – 73.57 million tonnes
1999–00: 45.16 million hectares – 89.68 million tonnes
2009–10: 41.92 million hectares – 89.1 million tonnes
2019–20: 43.66 million hectares – 118.87 million tonnes
2024–25: 51.42 million hectares – 150 million tonnes
India’s rice stocks exceed its requirements
– With increased production and procurement, central rice stocks have been rising steadily.
– As of January 1, 2026, central rice stocks (including unmilled paddy) stood at 63.06 million metric tonnes, far above buffer stock and public distribution requirements under the National Food Security Act, 2013.
Challenges of paddy cultivation
– Rice cultivation requires huge amounts of water—about 1–3 tonnes of water per 1 kg of rice.
– This leads to depletion of groundwater levels, excessive water use in water-scarce areas, and increased environmental impact.
Variation in productivity
– Productivity varies widely across states—higher in Punjab and Andhra Pradesh, lower in Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
Rising storage and government stocks
– Large state reserves and excess rice stocks are creating challenges in market pricing and logistics.
Government focus – crop diversification
– The government is encouraging farmers to move beyond rice to other crops to promote water conservation, crop diversity, nutrition, and income security.
– Financial incentives have been suggested for cultivating oilseeds, pulses, etc., instead of rice.
Exports and global positioning
– India is not only the largest producer but also the largest exporter of rice in the world.
– In 2025, rice exports reached 21.55 million metric tonnes, the second-highest level ever.
– Indian rice is exported to many countries, contributing to foreign exchange earnings.


