This is the current affairs of 12 to 15 February 2025. Here are questions and answers of daily current affairs for better preparation of competitive exams for government jobs.
PDF Download: Click here
1. What important agreements were signed during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the US?
– Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in Washington, D.C. on the evening of February 12, 2025 (Wednesday in the U.S., Thursday morning in India).
– A large number of Indians welcomed PM Modi outside Blair House.
– On February 14, 2025 (according to Indian time), PM Modi met with U.S. President Donald Trump at the White House, Washington D.C., and discussed various issues to strengthen India-U.S. relations.
Meeting with Elon Musk
– Prime Minister Narendra Modi held a bilateral meeting with SpaceX CEO Elon Musk at Blair House in Washington.
– Along with Elon Musk, PM Modi also met with Musk’s three children and gave them gifts.
– The meeting between PM Modi and Elon Musk covered topics such as space, mobility, technology, and innovation. During the meeting, discussions also took place regarding the launch of Starlink in India.
Topics Discussed:
1. $500 Billion Trade
– Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that India and the U.S. have set a target to double their trade to $500 billion (around ₹4,15,000 crores) by 2030. During his two-day visit to the U.S., Modi also mentioned that both countries will soon complete the work on a mutually beneficial trade agreement.
2. Issue of Illegal Immigrants in the U.S.
– PM Modi reiterated India’s stance on illegal immigration and said that if “people are living illegally in the U.S., India is ready to take them back.”
– He explained that most illegal immigrants come from ordinary families who are “shown big dreams, and many are sent to the U.S. through illegal means.”
– Supporting Trump, Modi said that to prevent human trafficking, the entire system needs to be uprooted, and the main fight is against this system. He expressed confidence that President Trump will help India in eliminating this system.
– This statement came a few weeks after over 100 immigrants were sent back from the U.S. military planes during Donald Trump’s second term.
– According to *Indian Express*, “We were handcuffed for 40 hours, our feet were chained, and we were not allowed to move an inch from our seat. After repeatedly requesting, we were allowed to drag ourselves to the restroom. Crew members would open the toilet door and push us inside.”
3. Terrorist Tahawwur Rana and the 26/11 Mumbai Attacks
– President Donald Trump decided to send the 26/11 Mumbai attack accused Tahawwur Rana to India. Welcoming this decision, Prime Minister Modi said, “I am grateful to the President for deciding to send such a criminal who caused great violence in India in 2008. India’s judiciary will take appropriate steps.”
4. India to Get F-35 Fighter Jets
– President Trump decided to provide India with F-35 fighter jets. This will make India one of the countries allowed to purchase the F-35 jets. Trump stated, “Starting this year, we will increase military sales to India and provide F-35 jets.”
5. MIGA and MAGA Fusion
– Prime Minister Modi shared his vision of “Make India Great Again” (MIGA), inspired by Trump’s “Make America Great Again” (MAGA). Modi said there will be a mega partnership between both countries.
6. India-China Border Issue
– President Trump spoke about the India-China border tension and the war in Ukraine. He said, “I understand India’s position and see the clashes happening on the border, which are very violent. I think these are still ongoing. If I can help, I would be happy to, as it needs to be stopped.”
7. Russia-Ukraine War
– Prime Minister Modi welcomed President Trump’s efforts to resolve the Russia-Ukraine conflict and reiterated India’s position that the resolution can only be achieved through dialogue. Modi said, “India is not neutral, we are always on the side of peace, and we have remained in contact with both countries.”
8. Civil Nuclear Agreement
– A joint statement said that both countries decided to enhance cooperation through localization and technology transfer for the construction of U.S.-designed nuclear reactors in India.
– In this regard, both countries reaffirmed their commitment to fully implement the U.S.-India 123 Civil Nuclear Agreement.
– The statement welcomed the amendments made by the Indian government in the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA), which will enhance cooperation in nuclear reactor construction and resolve civil liability issues.
9. Civil Space Cooperation
– India and the U.S. declared 2025 as an important year for civil space cooperation, which includes plans to send an Indian astronaut to the ISS and launch the “NISAR” mission. Additionally, there was focus on enhancing space exploration, flight safety, and commercial collaboration.
– Both countries expressed their commitment to advancing commercial space cooperation through industry participation in emerging areas such as connectivity, advanced spaceflight, satellites, space launch systems, space sustainability, space tourism, and advanced space manufacturing.
10. Quad Initiative
– Prime Minister Modi planned to invite President Trump to the Quad summit in New Delhi, where new initiatives on emergency assistance and maritime security will be discussed.
India-U.S. Bilateral Relations
Early Years (Post-Independence to the Cold War):
– India and the United States established formal diplomatic relations immediately after India’s independence in 1947. Following this, India adopted a non-alignment policy, maintaining general relations with both the Soviet Union and the U.S.
– However, during the Cold War, relations were often strained due to India’s non-alignment stance and its close ties with the Soviet Union, especially after the signing of the Indo-Soviet Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation Treaty in 1971.
Post-Cold War Relations:
– With the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union, India-U.S. relations gradually improved.
– In the 1990s, economic reforms in India opened opportunities for closer trade relations.
– After India’s nuclear tests in 1998, the two countries moved towards tense strategic relations, initially resulting in U.S. sanctions. However, relations began to improve after the Kargil War and U.S. President Bill Clinton’s visit in 2000.
Strategic Partnership (Post-2000s):
– A significant milestone in India-U.S. relations was the 2008 Civil Nuclear Agreement, which allowed India access to nuclear technology despite not signing the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). Since then, strategic partnerships have deepened in various areas, including defense, counter-terrorism, and energy.
U.S.-India Roadmap for Defense Industrial Cooperation:
– The U.S.-India roadmap for defense industrial cooperation, announced in 2023, is a comprehensive plan designed to promote defense cooperation between the two countries.
– It focuses on joint production and co-development of defense systems and technologies, with the aim of reducing India’s dependence on defense imports and promoting defense self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
Key Areas of India-U.S. Cooperation
Jet Engines:
– Joint production and technology transfer for fighter jet engines.
Unmanned Platforms:
– Co-development of drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
War Materiel and Ground Mobility Systems:
– Enhancing India’s capabilities in the production of ammunition and ground defense systems.
– This roadmap strengthens India’s defense capabilities while enhancing the strategic partnership between India and the U.S.
– It also opens doors for cooperation between defense companies in both countries to collaborate and develop cutting-edge technology for military applications.
—————–
2. In which country’s Marseille city did PM Modi inaugurate India’s new Consulate General?
a. France
b. America
c. New Zealand
d. South Africa
Answer: a. France
– On February 12, 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and French President Emmanuel Macron jointly inaugurated India’s new Consulate General in the French city of Marseille.
– The inauguration of the consulate marks a milestone in the bilateral relations between India and France.
– Prime Minister Modi concluded his three-day visit to France on February 12, 2025.
Jurisdiction of the Indian Consulate
– The jurisdiction of this Consulate General will cover four administrative regions in southern France: Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, Corsica, Occitanie, and Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.
– This region of France is renowned for trade, industry, energy, and tourism, and has strong economic, cultural, and people-to-people ties with India.
– The new consulate is located in France’s second-most populous city.
– It will further strengthen the multi-dimensional strategic partnership between India and France.
Tribute to Indian Martyrs
– On February 12, PM Modi visited the Mazargues War Memorial in Marseille, where he paid tribute to Indian soldiers who had fallen in World War I and World War II. Both PM Modi and President Macron honored the martyrs’ sacrifices and laid flowers in their memory.
– PM Modi also paid homage to Veer Savarkar during this visit.
——————-
3. How many MoUs were signed between the two (India-France) during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to France (10-12 February 2025)?
a. 5
b. 7
c. 8
d. 10
Answer: d. 10
During Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to France from February 10-12, 2025, 10 memorandums of understanding (MoUs) were signed between India and France in the fields of technology and innovation, science and technology, civil nuclear energy, Indo-Pacific/sustainable development, culture/people-to-people contact, and the environment.
List of Agreements
In the field of Technology and Innovation, Science and Technology:
1. India-France Declaration on Artificial Intelligence (AI).
2. Launch of the logo for India-France Innovation Year 2026.
3. Letter of Intent between the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, and the National Institute for Research in Computer Science and Automation (INRIA) France for the establishment of the Indo-French Centre for the Digital Sciences.
4. Agreement to host 10 Indian startups at the French startup incubator Station F.
In the field of Civil Nuclear Energy
5. Declaration of intent for establishing a partnership on advanced modular reactors and small modular reactors.
6. Renewal of the Memorandum of Understanding between the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), India, and the Commissariat for Atomic Energy and Alternative Energies of France (CEA), for collaboration with the Global Centre for Nuclear Energy Partnership (GCNEP).
7. Discussion on cooperation between India’s Department of Atomic Energy and France’s Atomic Energy Agency regarding the implementation agreement for GCNEP India and the Institute for Nuclear Science and Technology (INSTU), France.
In the field of Indo-Pacific/Sustainable Development:
8. Joint Declaration of Intent on Triangular Development Cooperation.
In the field of Culture/People-to-People Contact:
9. Joint inauguration of India’s Consulate General in Marseille.
In the field of Environment:
10. Declaration of intent on ecological transition, biodiversity, forests, marine affairs, and fisheries between the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change of India and the Ministry of Environment of France.
India-France Relations
-The relationship between India and France dates back to the 17th century when the French East India Company established trading posts in India. After India’s independence in 1947, France established diplomatic relations with India.
– India’s first strategic partnership agreement was signed in 1998.
– India has purchased submarines, helicopters, and missile systems from France, including the Rafale. The two countries also conduct joint military exercises.
– French investments are present in sectors like energy, transport, and defense, and over a thousand French companies are active in India.
– There is cooperation in nuclear energy (Jaitapur project) and solar energy (International Solar Alliance – ISA).
– Scientific cooperation includes space (ISRO-CNES) and academic exchanges.
– India and France signed a Transfer of Technology Agreement in 2005.
– France supported India’s ISA initiative, and the two countries jointly promoted environmental conservation efforts under the Paris Agreement in 2015.
– In 2015, India signed a deal with France for the purchase of 36 Rafale aircraft.
– Under this deal, several Rafale aircraft have already been delivered to India.
– In February 2022, India signed a roadmap with France to promote Blue Economy and Ocean Governance.
– In 2023, there was an agreement for additional purchase of Rafale aircraft, and a memorandum of understanding on joint satellite missions and space research between ISRO and CNES was signed.
France
– Capital – Paris
– President – Emmanuel Macron
– Prime Minister – François Bérurier
– Currency– Euro
– Neighboring Countries– Belgium, Luxembourg, Switzerland, Italy, Spain
– Maritime Border – United Kingdom
– Seas – Mediterranean Sea, Bay of Biscay, Celtic Sea, English Channel, North Sea
—————
4. Which rocket system did Prime Minister Narendra Modi offer to France during his visit to France (10-12 February 2025)?
a. Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV)
b.Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)
c. Pinaka multi-barrel rocket launch system (MBRLS)
d. Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
Answer: c. Pinaka multi-barrel rocket launch system (MBRLS)
Prime Minister Modi invited President Emmanuel Macron to closely observe the capabilities of the Pinaka system during their discussions.
Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) System
– The range of Pinaka MK1 is 38 kilometers.
– It can fire various types of ammunition.
– Efforts are underway to increase its range, which will extend to over 75 kilometers.
– The ultimate plan is to increase the range to 120 kilometers and eventually 300 kilometers.
– The name “Pinaka” is derived from the bow of the Hindu god Shiva.
– It was developed by DRDO in 1986. Since then, several advanced versions have been released.
– The production of Pinaka is carried out by Tata Advanced Systems and Larsen & Toubro (L&T).
—————–
5. What has the name of Fort William, the eastern headquarters of the Indian Army, been changed to?
a. Ajay Durg
b. Vijay Durg
c. Shivaji Durg
d. Bharat Durg
Answer: b. Vijaydurg (located in Kolkata)
– In addition, the name of Kitchenner House inside Fort William has been changed to Manekshaw House, and the South Gate, St. George Gate, has been renamed as Shivaji Gate.
– This was confirmed by the Chief Public Relations Officer of the Eastern Command, Wing Commander Himanshu Tiwari, in February 2025.
When was Fort William constructed?
– Fort William was constructed in 1781 by the British and was named after King William III of England.
– The new name, Vijay Durg, refers to a historic fort in Maharashtra (Vijaydurg Fort on the Sindhudurg coast) that served as a naval base for the Marathas.
Vijaydurg Fort
– It is the oldest fort located on the Sindhudurg coast, built during the reign of King Bhoj II of the Shilahar dynasty (1193-1205). Later, Shivaji renovated it.
————–
6. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)’s Hindustan Jet Trainer HJT-36 has been renamed as what?
a. Ajay
b. Yashas
c. Safal
d. Shakti
Answer: b.Yashas
– The Chairman and Managing Director of HAL, Dr. Sunil, stated that the name of the Hindustan Jet Trainer HJT-36 has been changed to Yashas.
– This was confirmed on February 10, 2025.
– The defense PSU stated that significant changes have been made to improve the departure characteristics and spin resistance of the trainer aircraft.
About HAL HJT-36 (Yashas):
– It is a subsonic intermediate jet trainer aircraft, designed and developed by the Aircraft Research and Design Centre (ARDC), and manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force and Indian Navy.
Has Yashas been upgraded?
– To be inducted into service, the aircraft has been equipped with new technological avionics and a state-of-the-art cockpit. As a result, training effectiveness and operational capability will increase, while weight will decrease, and the issue of outdated imported equipment will be resolved through Indian Line Replaceable Units (LRU).
– HAL mentioned that Yashas is capable of Stage-2 pilot training, counter-terrorism operations, surface force operations, weapons training, aerobatics, etc.
– The capabilities of HJT-36 include stall and spin resistance, aerobatics, a capacity to carry up to 1000 kilograms of armament, and the ability to refuel and de-fuel at a single point on the ground.
—————
7. According to the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024 report, which country has the most corruption?
a. Somalia.
b. South Sudan.
c. Syria.
d. India
Answer: b. South Sudan.
– The Transparency International’s Corruption Report for 180 countries was released on February 11, 2025.
– In this ranking, the country ranked 1st has the least corruption, and the country ranked 180th has the most corruption.
– According to the report, South Sudan (180) is the most corrupt country.
– For this index, Transparency International’s experts assess corruption in the public sector of each country.
– After that, each country is given a score between 0 to 100.
– The more corruption a country has, the lower its score is.
– Based on this, the ranking in the index is determined.
– The country with the highest corruption is South Sudan, which received a score of 8.
– Following this, Somalia scored 9, Venezuela scored 10, Syria scored 12, and Yemen scored 13.
Top 10 Most Corrupt Countries:
Rank – Country – Score
– 170 – Sudan – 15
– 172 – Nicaragua – 14
– 173 – Equatorial Guinea – 13
– 173 – Eritrea – 13
– 173 – Libya – 13
– 173 – Yemen – 13
– 177 – Syria – 12
– 178 – Venezuela – 10
– 179 – Somalia – 9
– 180 – South Sudan – 8
——————
8. Which is the least corrupt country according to Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024?
a. New Zealand
b. Finland.
c. Denmark.
d. India
Answer: c. Denmark
– In this corruption-related report, Denmark has topped the list with a score of 90, meaning Denmark is the least corrupt country.
– Denmark has been ranked as the least corrupt country for the seventh consecutive time.
Top 10 Least Corrupt Countries:
Rank – Country – Score
– 1 – Denmark – 90
– 2 – Finland – 88
– 3 – Singapore – 84
– 4 – New Zealand – 83
– 5 – Luxembourg – 81
– 5 – Norway – 81
– 5 – Switzerland – 81
– 8 – Sweden – 80
– 9 – Netherlands – 78
– 10 – Australia – 77
– 10 – Iceland – 77
– 10 – Ireland – 77
– 96 – India – 38 (Previous score was 39)
—————
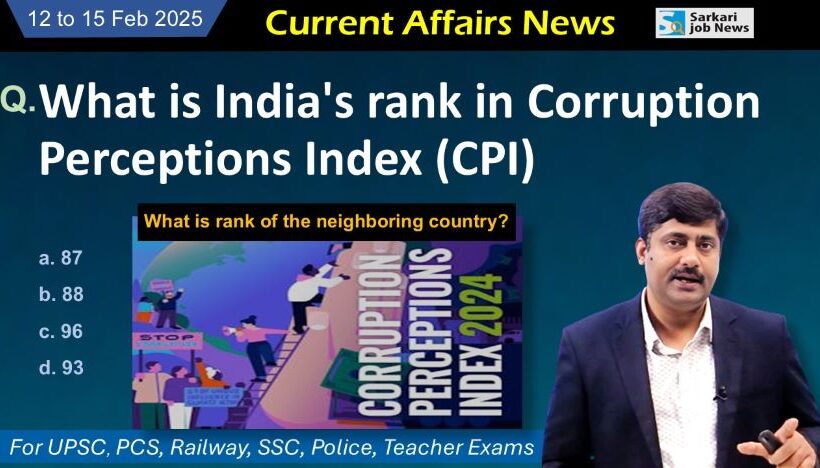
9. What is India’s ranking in Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024?
a. 87
b. 88
c. 96
d. 93
Answer: c. 96
– In the Transparency International 2024 Index, India dropped three positions and ranked 96th among 180 countries.
– In 2024, India’s overall score was 38, while it was 39 in 2023. This indicates an increase in corruption in the country.
– In 2023, India’s rank was 93, while this time the report shows a rank of 96.
India’s Neighboring Countries:
– Myanmar (168)
– Afghanistan (165)
– Bangladesh (151)
– Pakistan (135)
– Sri Lanka (121)
– Nepal (107)
– Maldives (96) [India’s rank is also 96.]
– China (76)
– Bhutan (18) [Bhutan has less corruption.]
————–
10. Mahant Satyendra Das, the chief priest of which major temple, passed away on 12 February 2025?
a. Vaishno Devi
b. Ram Janmabhoomi Temple
c. Kashi Vishwanath
d. Kedarnath
Answer: b. Ram Janmabhoomi Temple
– He was the chief priest of the Ram Janmabhoomi temple in Ayodhya.
– He was 85 years old and was admitted to the hospital in critical condition on February 3.
—————
11. Which state will host the 39th National Games?
a. Delhi
b. Meghalaya.
c. Haryana
d. Uttarakhand.
Answer: b. Meghalaya.
– The Indian Olympic Association (IOA) confirmed in a letter written to Chief Minister Conrad K. Sangma on February 10, 2025.
– The 39th National Games will be held in February-March 2027.
– Note: The 38th National Games were held from January 28 to February 14, 2025, in Dehradun, Uttarakhand. On February 14, during the closing ceremony of the 38th National Games in Haldwani, Uttarakhand, the IOA will officially hand over the flag to Meghalaya.
National Games:
– The National Games were first held in 1924 in Lahore, British India.
– At that time, they were known as the “All India Olympic Games.”
– In 1940, the tournament was renamed “National Games.”
– After independence, they were first held in Lucknow in 1948.
– The Indian Olympic Association (IOA) organizes the event.
– The president of the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) is P.T. Usha.
Meghalaya:
– Capital: Shillong
– Governor: CH Vijayashankar
– Chief Minister: Conrad Sangma
—————–
12. Where did the Joint Special Forces Exercise Cyclone-III between India-Egypt start?
a. Rajasthan, India
b. Luxor, Egypt
c. Agra, Uttar Pradesh
d. Alexandria, Egypt
Answer: a. Rajasthan, India
– This time, Cyclone-III Exercise is the third edition. It will take place from February 10 to February 23, 2025.
– The second edition of this exercise was held in January 2024 in Egypt.
– The first edition was held in India in 2023.
– It is an annual event that alternates between India and Egypt.
Who represented India?
– The Indian delegation consists of 25 soldiers, represented by soldiers from two special forces battalions.
– The Egyptian delegation also consists of 25 soldiers, represented by special forces groups and task force soldiers from Egypt.
Objective of Cyclone-III:
– The objective is to strengthen military relations between the two countries through mutual cooperation, unity, and the exchange of special operations strategies. Special attention will be given to physical fitness, joint planning, and tactical exercises.
– The exercise will involve strategic training and verification in desert and semi-desert areas to fight terrorism.
– There will also be a demonstration of indigenous military equipment and an inspection of Egypt’s defense manufacturing industry.
Egypt:
– President: Abdel Fattah el-Sisi
– Capital: Cairo
—————
13. When was the International Epilepsy Day observed in the year 2025?
a. 10 February
b. 12 February
c. 14 February
d. 15 February
Answer: a. 10 February
– It is celebrated on the second Monday of February.
– In the year 2025, it was celebrated on 10 February.
– Its purpose is to promote correct facts and better treatment about epilepsy.
– National Epilepsy Day: 17 November
————–
14. When is the International Day of Women and Girls in Science observed?
a. 8 February
b. 9 February
c. 10 February
d. 11 February
Answer: d. 11 February
– This day was declared by the United Nations General Assembly in the year 2015.
– It was first organized in the year 2016.
– Its purpose is to remember the contribution of women and girls in the field of science and technology.
– Also, women and girls are inspired for this field.
————-
15. When is World Radio Day celebrated?
a. 11 February
b. 12 February
c. 13 February
d. 14 February
Answer: c. 13 February
Theme 2025 :
“Radio and Climate Change.”
– On this day in the year 1945, the first broadcast was made from United Nations Radio.
– Its purpose is to promote radio.
– Also, people are encouraged to use it.
– It was announced by UNESCO in the year 2011.
– In the year 2012, the United Nations General Assembly adopted it as an international day.
—————
16. When is Indian National Women’s Day celebrated?
a. 11 February
b. 12 February
c. 13 February
d. 14 February
Answer: c. 13 February
– This day is celebrated on the birth anniversary of Sarojini Naidu.
– She was born on February 13, 1879.
Sarojini Naidu’s nicknames
1. Nightingale of India
2. Bharat Kokila
– Sarojini Naidu had an important contribution in India’s freedom struggle.
– Sarojini Naidu became the President of the Indian National Congress in the year 1925.
– She was the first Indian woman to become the President of the Indian National Congress.
– Sarojini Naidu led the Civil Disobedience Movement and the Quit India Movement.
Note – International Women’s Day is celebrated every year on March 8.