This is the current affairs of 11 & 12 December 2025. Here are questions and answers of daily current affairs for better preparation of competitive exams for government jobs.
PDF Download: Click here
1. According to the World Inequality Report 2026, what percentage of India’s total income is held by the top 1% of its population?
a. 22.6%
b. 57.7%
c. 27.3%
d. 15.0%
Answer: a. 22.6% (Income inequality in India is the highest in the world)
– The World Inequality Report 2026 was released in December 2025 by the World Inequality Lab.
– This report has been prepared in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
– Income inequality in India is the highest in the world.
————–
2. According to the World Inequality Report 2026, what percentage of India’s total income is earned by the top 10 percent of its population?
a. 22.6%
b. 57.7%
c. 27.3%
d. 15.0%
Answer: b. 57.7% (Income inequality in India is the highest in the world)
– The World Inequality Report 2026 was released in December 2025 by the World Inequality Lab.
– This report has been prepared in collaboration with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
– The report has been edited by economists Lucas Chancel, Ricardo Gomez-Carrera, Rowaida Moshrif, and Thomas Piketty.
– The World Inequality Report 2026, which is the third report in this series after the 2018 and 2022 editions, is based on the work of more than 200 scholars worldwide associated with the World Inequality Lab.
World Inequality Report 2026
– Income inequality in India is the highest in the world.
– The top 10 percent earners hold 58 percent of national income, while the bottom 50 percent receive only 15 percent.
– Wealth inequality in India is even higher, with the richest 10 percent holding about 65 percent of total wealth, and the top 1 percent holding about 40 percent.
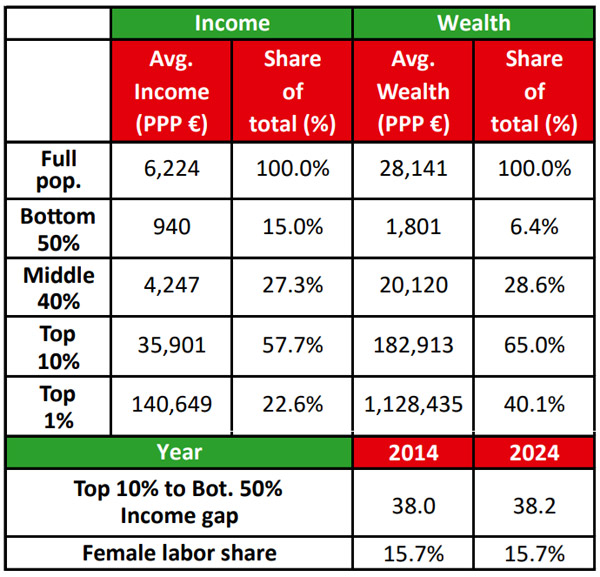
Income and wealth inequality in India
Population — Income — Wealth
– Top 1%: 22.6%, 40.1%
– Top 10%: 57.7%, 65.0%
– Middle 40%: 27.3%, 28.6%
– Bottom 50%: 15.0%, 6.4%
Note – As per the earlier World Inequality Report 2022, the top 10 percent in India held 57 percent of total national income, while the bottom 50 percent held 13 percent in 2021.
What is the global status of inequality?
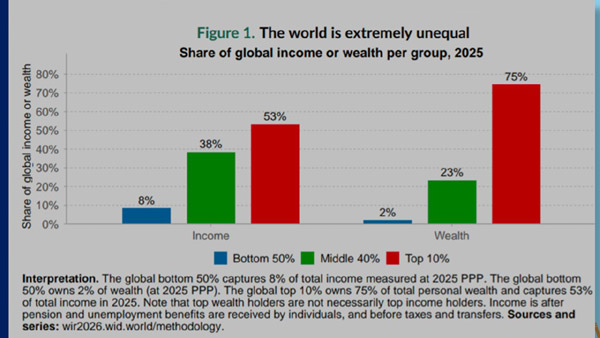
– The richest 0.001% of the world own three times more wealth than the poorest 50%. That is, 56,000 people own three times more wealth than the bottom four billion people.
– The richest 10% of the world’s population hold 75% of the wealth, while the bottom 50% hold only 2% of the wealth.
– The top 10% take 53% of income, the middle 40% take 38%, and the bottom 50% are left with the rest.
– The world’s top 100,000 people collectively own 3% of global wealth, which is more than the wealth owned by the bottom half of the world’s adult population.
– These figures highlight that today’s inequality is driven not only by the gap between the rich and poor, but also by the widening gap within the top class.
—————
3. Through Trump’s mediation, a peace agreement was reached between Rwanda and which country, raising hopes of ending the 30-year-old conflict there?
a. Uganda
b. Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
c. Tanzania
d. Burundi
Answer: b. Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)
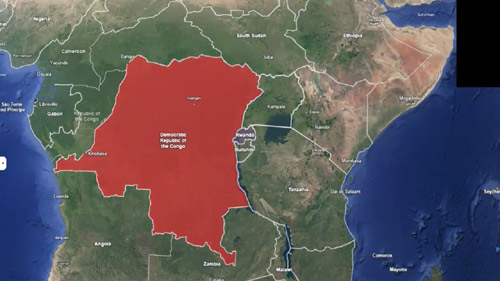
– U.S. President Donald Trump mediated this agreement between two African countries on December 4, 2025.
– Rwanda’s President Paul Kagame and DRC’s President Félix Tshisekedi signed the agreement.
– Trump said that this agreement would open the way for American companies to access Central Africa’s rare-earth minerals.
– However, despite the agreement, violence continues on the ground in eastern Congo.
– The DRC is one of the world’s richest mineral-resource countries, but these resources have led to violence, human rights violations, and political instability.
Congo plagued by decades of conflict
– The Central African country DRC has been suffering for decades from conflict involving more than 100 armed groups.
– The conflict began after the 1994 genocide in Rwanda, where Hutu militias killed 500,000 to 1 million ethnic Tutsis, moderate Hutus, and Twa indigenous people.
– When Tutsi-led forces retaliated, two million Hutus fled to Congo out of fear of retaliation.
– Rwandan authorities accuse these fleeing Hutus of participating in the genocide.
– M23 has become the most powerful Rwanda-backed rebel group in Congo.
– In June 2025, the conflict escalated when M23 captured major cities Goma and Bukavu.
– These cities border Rwanda. Population is two million. Near the city is Lake Kivu, half in DRC and half in Rwanda.
– The conflict has displaced millions and made conditions even worse.
Congo’s mineral wealth
– Cobalt: DRC is the world’s largest cobalt producer (about 70% of global output). Used in EV batteries, smartphone and laptop batteries, aircraft, and military equipment.
– Copper: DRC is one of the world’s largest copper producers. Used in electrical wiring, construction, and electronics.
– Coltan: DRC holds about 60% of the world’s coltan reserves. Used in mobile phones, laptops, electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
– Tungsten: Found in large quantities. Used in industrial machinery, light bulbs, electronic chips, and weapons.
– Tin: Used in food packaging (canning), electronic circuit boards, and soldering.
– Diamonds: DRC is the largest producer of industrial diamonds. Used in jewelry and industrial cutting/drilling equipment.
– Gold: Large reserves, especially in the east. Used in jewelry, investment, electronics, and medical devices.
What now?
– Violence by Rwanda-backed groups in DRC has not stopped, but because of Trump’s mediated agreement, DRC will have to hand over a large part of its mines to American companies.
—————
4. Which country was the first in the world to ban social media for children under the age of 16?
a. New Zealand
b. Australia
c. France
d. Germany
Answer: b. Australia
– On December 10, 2025, Australia implemented the world’s first strict law banning major social media platforms (like TikTok, YouTube, Instagram, and Facebook) for children under 16.
– This step has been taken to address mental-health crises, cyberbullying, and excessive screen time.
Key facts and timeline
– Australia’s new law was passed in 2024 and came into force on December 10, 2025.
– The law orders 10 major platforms to block users under 16.
– Violations can result in fines of 49.5 million Australian dollars (around 33 million USD).
Status in other countries
– Globally, the trend is spreading fast.
– The EU passed a proposal in November 2024 setting a minimum age of 16, while the UK’s Online Safety Act (2023) focuses on harmful content.
– Germany, France, and Italy require parental consent for ages 13–15, while Norway and Denmark plan to restrict usage below 15.
– The U.S. COPPA bans data collection under age 13, but challenges exist at state level.
– China limits screen time through “minor mode”, and Malaysia will impose a below-16 ban from 2026.
Technical challenges
– Age verification risks privacy violations, such as surveillance via facial recognition.
– Meta argues that a “complete ban” may isolate teenagers, especially queer or niche-interest communities.
– A 14-year-old Australian girl, Annie Wang, said: “This will be bad for queer people and those with niche interests, because social media is their community.”
– Studies show that 86% of Australian children aged 8-15 were already using social media, which could cause revenue losses and disrupt user-growth pipelines for platforms.
Why the ban was imposed
– In the digital era, social media has revolutionized communication, but it is severely affecting children’s mental health, privacy, and social development.
– An Indian is present on at least 11 social-media platforms
– According to research firm Redseer, Indian users spend an average of 7.3 hours daily on smartphones — most of it on social media.
– U.S. users average 7.1 hours, and Chinese users 5.3 hours.
Australia
– Capital: Canberra
– Prime Minister: Anthony Albanese
– Currency: Australian Dollar
– Population: 27.5 million
—————
5. In which African country did soldiers claim to have staged a coup in December 2025, which the government later thwarted?
a. Benin
b. Nigeria
c. Togo
d. Burkina Faso
Answer: a. Benin

– On December 7, 2025, a group of soldiers in Benin suddenly appeared on the state TV channel and announced the immediate dissolution of the government.
– The group called itself the “Military Committee for Re-foundation.”
– The committee claimed to have removed the president and all constitutional institutions and appointed Lieutenant Colonel Pascal Tigri as its new head.
– Shortly afterward, the Benin government denied these claims.
– Foreign Minister Olusegun Adaji Bakari said the rebels had seized only the national TV station, which went off-air for a few minutes.
– According to the Interior Minister, security forces foiled the attempt in time and the coup was thwarted.
Political situation
– Benin is considered a model of democracy. Although the country witnessed several coup attempts after gaining independence from France in 1960, none succeeded after 1972.
– President Patrice Talon had been in power since 2016 and was to step down in April 2026.
– His expected successor, former Finance Minister Romuald Wadagni, was leading the polls.
– Opposition candidate Renaud Agbodjo was rejected by the election commission due to insufficient support.
– In November 2025, Parliament extended the presidential term from five to seven years, while keeping the term limit at two.
– In such a situation, the coup attempt is considered a major turning point in Benin’s politics.
– In recent years, Niger, Burkina Faso, and Mali have seen successful coups.
Coup-like situations near India
– Similarly, in India’s neighbouring country Bangladesh, students led a coup-like uprising in 2024. PM Sheikh Hasina had to flee the country, and an interim government led by Muhammad Yunus is currently in power.
– In 2025, a coup occurred in Nepal after Gen-Z protests, although the army did not seize power.
– Sri Lanka has also faced a similar situation—later an elected government returned.
– Earlier in 2021, Myanmar’s military staged a coup.
List: Coups in African countries
– Gabon: August 2023
– Niger: July 2023
– Burkina Faso: January 2022
– Guinea: September 2021
– Chad: April 2021
– Mali: August 2020
– Sudan: April 2019
Benin
– Capital: Porto-Novo
– President: Patrice Talon
– Currency: CFA Franc
– Official language: French
– Neighbouring countries: Togo, Burkina Faso (military rule), Niger (military rule), Nigeria
– Sea: Gulf of Guinea (part of the Atlantic Ocean)
—————
6. Who has become the new Prime Minister of the Czech Republic?
a. Petr Pavel
b. Petr Fiala
c. Roger Federer
d. Andrej Babis
Answer: d. Andrej Babis

– Andrej Babis is a 71-year-old billionaire businessman.
– He took oath as the new Prime Minister of the Czech Republic on 9 December 2025.
– He had earlier served as Prime Minister from 2017 to 2021.
– He owns about 200 companies under the Agrofert group.
– He publicly announced that he would get rid of his major businesses to avoid conflicts of interest arising from his private dealings and his political position.
Czech Republic (This is a land-locked European country)
– Capital – Prague
– President – Petr Pavel
– Prime Minister – Andrej Babis
– Currency – Czech Koruna
– Neighbouring countries – Germany, Poland, Slovakia, Austria
—————-
7. India hosted the Squash World Cup for the third consecutive time, but in which city was it held in 2025?
a. Mumbai
b. Chennai
c. Madurai
d. Delhi
Answer: b. Chennai
– This tournament was held from 10 to 14 December 2025 at the SDAT Stadium, Chennai.
—————
8. When is Armed Forces Flag Day celebrated?
a. 4 December
b. 5 December
c. 6 December
d. 7 December
Answer: d. 7 December
– Armed Forces Flag Day is celebrated every year on 7 December in India.
– This day is dedicated to expressing respect towards the brave soldiers of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, ex-servicemen, and the families of martyrs.
– It has been observed annually since 1949.
– That year, the Government of India declared this day as a means to raise funds for soldiers’ welfare.
—————
9. When is International Civil Aviation Day celebrated?
a. 4 December
b. 5 December
c. 6 December
d. 7 December
Answer: d. 7 December
Theme for 2025
– Safe Skies and a Sustainable Future for All
– International Civil Aviation Day is observed every year on 7 December.
– The purpose of this day is to spread awareness about the importance of international civil aviation for social and economic development in the world.
– This day is observed by the International Civil Aviation Organization.
– It was proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly in 1996.
International Civil Aviation Organization
– Established – 7 December 1944
– Headquarters – Montreal, Canada
—————-
10. When is the International Anti-Corruption Day observed?
a. 9 December
b. 14 December
c. 15 December
d. 16 December
Answer: a. 9 December
Theme for 2025
– Uniting with Youth Against Corruption: Shaping Tomorrow’s Integrity.
– The purpose of this day is to raise awareness about the serious impacts of corruption and to promote transparency, accountability, and integrity in governance and society.
– This day was declared by the United Nations General Assembly in 2003.
—————-
11. When is the International Day for Remembrance and Prevention of Genocide Victims observed?
a. 9 December
b. 14 December
c. 15 December
d. 16 December
Answer: a. 9 December
– The United Nations General Assembly declared this day in 2015.
– Genocide is defined as acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group. These include:
What is genocide?
– According to the UN Genocide Convention, genocide means the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group through acts such as—
– Killing members of the group
– Causing serious bodily or mental harm
– Imposing conditions intended to bring about the group’s physical destruction
– Preventing births or forcibly transferring children
Genocide is considered one of the most heinous atrocities, alongside war crimes, crimes against humanity, and ethnic cleansing.


