This is the current affairs of 11 June 2024. Here are questions and answers of daily current affairs for better preparation of competitive exams for government jobs.
PDF Download: Click here
Narendra Modi
– Prime Minister and also in-charge of:
– Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions;
– Department of Atomic Energy;
– Department of Space;
– All important policy issues; and
– All other portfolios not allocated to any Minister.
—-
CABINET MINISTERS
1. Raj Nath Singh: Minister of Defence.
2. Amit Shah: Minister of Home Affairs; and Minister of Cooperation
3. Nitin Jairam Gadkari: Minister of Road Transport and Highways
4. Jagat Prakash Nadda:
– Minister of Health and Family Welfare; and
– Minister of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
5. Shivraj Singh Chouhan
– Minister of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare;
– Minister of Rural Development.
6. Nirmala Sitharaman
– Minister of Finance;
– Minister of Corporate Affairs
7. Dr. Subrahmanyam Jaishankar
– Minister of External Affairs.
8. Manohar Lal
– Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs;
– Minister of Power
9. H. D. Kumaraswamy
– Minister of Heavy Industries;
– Minister of Steel
10. Piyush Goyal
– Minister of Commerce and Industry.
11. Dharmendra Pradhan
– Minister of Education
12. Jitan Ram Manjhi
– Minister of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
13. Rajiv Ranjan Singh alias Lalan Singh
– Minister of Panchayati Raj;
– Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying
14. Sarbananda Sonowal
– Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways
15. Dr. Virendra Kumar
– Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment
16. Kinjarapu Rammohan Naidu
– Minister of Civil Aviation.
17. Pralhad Joshi
– Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution;
– Minister of New and Renewable Energy
18. Jual Oram
– Minister of Tribal Affairs
19. Giriraj Singh
– Minister of Textiles
20. Ashwini Vaishnaw
– Minister of Railways;
– Minister of Information and Broadcasting;
– Minister of Electronics and Information Technology
21. Jyotiraditya M. Scindia
– Minister of Communications;
– Minister of Development of North Eastern Region
22. Bhupender Yadav
– Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
23. Gajendra Singh Shekhawat
– Minister of Culture;
– Minister of Tourism.
24. Annpurna Devi
– Minister of Women and Child Development
25. Kiren Rijiju
– Minister of Parliamentary Affairs;
– Minister of Minority Affairs.
26.Hardeep Singh Puri
– Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas
27. Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya
– Minister of Labour and Employment; and
– Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports.
28. G. Kishan Reddy
– Minister of Coal;
– Minister of Mines.
29. Chirag Paswan
– Minister of Food Processing Industries
30. C R Patil
– Minister of Jal Shakti
—-
MINISTERS OF STATE (INDEPENDENT CHARGE)
1. Rao Inderjit Singh
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation;
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Planning;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Culture.
2. Dr. Jitendra Singh
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Science and Technology;
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Earth Sciences;
– Minister of State in the Prime Minister’s Office;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions;
– Minister of State in the Department of Atomic Energy; and
– Minister of State in the Department of Space.
3. Arjun Ram Meghwal
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Law and Justice; and
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs.
4. Jadhav Prataprao Ganpatrao
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Ayush;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
5. Jayant Chaudhary
– Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Education.

—-
MINISTERS OF STATE
1. Jitin Prasada
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Commerce and Industry;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
2. Shripad Yesso Naik
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Power;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
3. Pankaj Chaudhary
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Finance
4.Krishan Pal
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Cooperation
5. Ramdas Athawale
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
6. Ram Nath Thakur
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
7. Nityanand Rai
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Home Affairs
8. Anupriya Patel
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
9. V. Somanna
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Jal Shakti;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Railways.
10. Dr. Chandra Sekhar Pemmasani
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Rural Development;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Communications.
11. Prof. S. P. Singh Baghel
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
12. Sushri Shobha Karandlaje
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
13. Kirtivardhan Singh
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of External Affairs
14. B. L. Verma
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
15. Shantanu Thakur
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
16. Suresh Gopi
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Tourism.
17. Dr. L. Murugan
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs
18. Ajay Tamta
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
19. Bandi Sanjay Kumar
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Home Affairs.
20. Kamlesh Paswan
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Rural Development
21. Bhagirath Choudhary
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
22. Satish Chandra Dubey
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Coal;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Mines.
23. Sanjay Seth
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Defence.
24. Ravneet Singh
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Food Processing Industries;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Railways
25. Durgadas Uikey
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Tribal Affairs
26. Raksha Nikhil Khadse
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
27. Sukanta Majumdar
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Education; and
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region.
28. Savitri Thakur
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Women and Child Development
29. Tokhan Sahu
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
30. Raj Bhushan Choudhary
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Jal Shakti
31. Bhupathi Raju Srinivasa Varma
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Heavy Industries;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Steel.
32. Harsh Malhotra
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Corporate Affairs;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
33. Nimuben Jayantibhai Bambhaniya
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
34. Murlidhar Mohol
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Cooperation;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
35. George Kurian
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Minority Affairs;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
36. Pabitra Margherita
– Minister of State in the Ministry of External Affairs;
– Minister of State in the Ministry of Textiles
————-
————-
2. Name the youngest minister ever in the Union Cabinet?
a. Pemmasani Chandrasekhar
b. Ram Mohan Naidu
c. Bhupatiraju Srinivas
d. Sanjana Jatav
Answer: b. Ram Mohan Naidu

– According to several media reports, including The Hindu, Ram Mohan Naidu is the youngest minister in the history of the central cabinet.
– He is a leader of the TDP (Telugu Desam Party).
– Having been an MP from the Srikakulam Lok Sabha seat in Andhra Pradesh three times, Ram Mohan Naidu has become the youngest central minister.
– He is currently 36 years old.
– Ram Mohan Naidu won the 2024 Lok Sabha election with a huge majority of over 327,000 votes.
– Ram Mohan Naidu is the son of former central minister and TDP leader Yerran Naidu.
– His father, Yerran Naidu, became the youngest cabinet minister in 1996.
– Now, in 2024, Ram Mohan Naidu has become a minister in the NDA coalition government and has broken his father’s record.
————–
3. Under which scheme, in the first meeting of the cabinet during the third term of Prime Minister Modi, it was decided to build 3 crore houses for the poor?
a. Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana
b. MGNREGA
c. Suryodaya Yojana
d. Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana
Answer: d. Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)

– In its first meeting on June 10, 2024, the central cabinet approved the construction of 30 million rural and urban homes for the poor.
– These homes, to be built in villages and cities under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, will have toilets, electricity, water, and gas connections.
The scheme started in 2015-16
– The central government started this scheme in 2015-16 to assist eligible rural and urban families in constructing homes with basic amenities.
– A total of 42.1 million homes have already been built under this scheme in the past 10 years.
– Financial assistance for building homes under the scheme is provided by both the central and state governments.
————–
4. Sikkim Chief Minister Prem Tamang took oath as Chief Minister on June 10, for which 50th time he became the leader to hold this post?
a. Second
b. First
c. Third
d. Fourth
Answer: a. Second
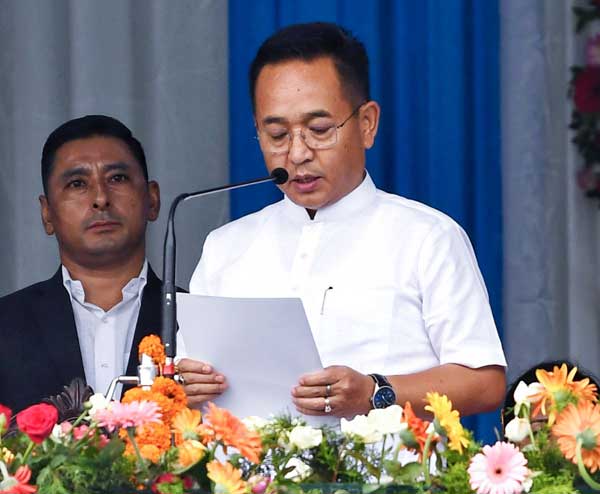

– On June 10, 2024, Prem Singh Tamang, the convener of the Sikkim Krantikari Morcha (SKM), was sworn in as the state’s Chief Minister for the second time.
– He is popularly known as PS Golay in the state.
– Sikkim’s Governor Lakshman Prasad Acharya administered the oath of office at a ceremony held at Paljor Stadium in the capital, Gangtok.
– The assembly elections in Sikkim were held on April 19, 2024, and the results were announced on June 2.
– In these elections, the party of 56-year-old Prem Singh Tamang, SKM, won 31 out of 32 seats.
– The opposition, the Sikkim Democratic Front (SDF), which had been in power in the state for a continuous 25 years until 2019, won only one seat.
Tamang Became CM After Being Released From Jail
– Prem Singh Tamang was once considered a close associate of SDF Chief Minister Pawan Kumar Chamling.
– Tamang rebelled against him and formed the SKM party in 2013.
– In the 2014 assembly elections, SKM won 10 seats.
– In 2016, Tamang was found guilty of embezzling government funds between 1994 and 1999, leading to his disqualification.
– He was in jail from 2016 to 2018, after which he contested the election and became the Chief Minister.
– Population: 540,493
– Languages: Nepali, Bhutia, and Lepcha
– Neighboring State: West Bengal
—————
5. Which player won the Norway Chess 2024 men’s title?
a. Magnus Carlsen
b. Praggnanandhaa
c. Fabiano Caruana
d. Hikaru Nakamura
Answer: a. Magnus Carlsen

– On June 7, 2024, the world’s number one player, Norway’s Magnus Carlsen, defeated Fabiano Caruana in a match to claim the title.
– As the winner, he received a prize of approximately 65,000 dollars.
Women’s Title
– In the women’s category of Norway Chess, world champion Wenjun Ju of China defeated Pia Cramling of Sweden to gain a lead with 14.5 points.
—————
6. Who has become the first woman helicopter pilot of the Indian Navy?
a. Anamika B Rajeev
b. Monica Rajan
c. Abhilasha Barak
d. Sarla Mati
Answer: a. Anamika B Rajeev

– Sub-Lieutenant Anamika B Rajeev has become the first female helicopter pilot in the Indian Navy.
– The passing-out parade was held on June 8, 2024, at INS Rajali in Arakkonam, Tamil Nadu.
– At the event, Anamika B Rajeev was honored with the ‘Gold Wings’ by Vice Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the Eastern Naval Command.
– Anamika will be permitted to fly helicopters such as Sea Kings, HAL Dhruv, Chetak, and MH-60R Seahawks.
– In a statement, the Navy said, “Highlighting the Indian Navy’s commitment to gender inclusivity and expanding career opportunities for women, Sub-Lieutenant Anamika B Rajeev has made history by graduating as the first female naval helicopter pilot.”
First Female Pilots in the Armed Forces
– Indian Air Force’s first female fighter pilot – Avani Chaturvedi
– First female pilot of the Rafale aircraft – Shivangi Singh
– Indian Army’s first female fighter pilot – Abhilasha Barak
– Indian Navy’s first female helicopter pilot – Anamika B Rajeev
How to Become a Pilot in the Armed Forces
– To enter the Army, Navy, or Air Force, one must take the NDA, NCC Special Entry, AFCAT, or CDS exams.
– After passing any of these exams, you can become a fighter pilot if you wish.
– For this, you need to complete a graduation course from the Combat Army Aviation Training School in Nashik.
– After that, you can become a fighter, transport, or helicopter pilot.
Navy Chief
– Admiral Radhakrishnan Hari Kumar

—————
7. Which player won the men’s singles title at French Open 2024?
a. Alexander Zverev
b. Carlos Alcaraz
c. Casper Ruud
d. Yannick Sinner
Answer: b. Carlos Alcaraz

– Spanish player Carlos Alcaraz won his third Grand Slam title by defeating Germany’s Alexander Zverev in the men’s singles final of the French Open.
– However, this was his first title at the French Open.
– The final match took place on June 9, 2024.
– With this victory, he also became the youngest player to win three Grand Slam titles.
– Alcaraz claimed the US Open title in 2022 by defeating Norway’s Casper Ruud.
– In 2023, he succeeded in winning the Wimbledon title by defeating Novak Djokovic.
– This was the first French Open final since 2004 in which Rafael Nadal, Novak Djokovic, or Roger Federer did not play.
Men’s Doubles Title
– Marcelo Arévalo of El Salvador and Mate Pavić of Croatia won the French Open men’s doubles final by defeating Italy’s Simone Bolelli and Andrea Vavassori 7-5, 6-3.
How Many Grand Slams Are There?
1. Australian Open
2. French Open
3. Wimbledon
4. US Open
—————
8. Which player won the women’s singles title at French Open 2024?
a. Katerina Siniakova
b. Justine Henin
c. Jasmine Paolini
d. Iga Swiatek
Answer: d. Iga Swiatek

– She is a star from Poland and the world number one player.
– On June 8, 2024, she defeated Italy’s Jasmine Paolini to win the French Open title.
– This was her fourth French Open title. She was also the champion in 2020, 2022, and 2023.
– In addition to this, Iga Swiatek has also won the US Open title in 2022.
French Open 2024 Women’s Doubles
– The pairing of Coco Gauff from the United States and Katerina Siniakova from the Czech Republic defeated Italy’s Sara Errani and Jasmine Paolini to win the women’s doubles title.
– This is the first women’s doubles Grand Slam title for America’s Coco Gauff.
—————
9. Which Indian won the gold medal in the men’s 10m air pistol event at the ISSF World Cup 2024 (held in Munich)?
a. Sifat Kaur
b. Sarabjot Singh
c. Navneet Pandya
d. Vijay Chauhan
Answer: b. Sarabjot Singh (22 years old)

– Indian shooter Sarabjot Singh won the gold medal in the men’s 10-meter air pistol event at the ISSF World Cup 2024 on June 6, 2024.
– Sarabjot Singh scored 242.7 points in the final to clinch the gold medal.
– He defeated China’s Shuaihang Bu in this competition.
– After last year’s World Cup in Bhopal, this was Sarabjot’s second individual gold medal.
Note: This championship took place in Munich, Germany from May 31 to June 8, 2024.
International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF):
– The ISSF is the governing body for Olympic shooting programs and several non-Olympic shooting sports in rifle, pistol, and shotgun (clay target) disciplines.
– Established in 1907 as the International Shooting Union, it later changed its name to ISSF in 1998.
– The headquarters of the ISSF is located in Munich, Germany, and the President is Luciano Rossi.
—————
10. India and which countries and union formed the Biopharmaceutical Alliance?
a. USA, South Korea
b. Japan, European Union (EU)
c. Both a and b
d. Pakistan and Afghanistan
Answer: c. Both a and b [USA, South Korea, Japan, European Union (EU)]
– The aim of this alliance is to prevent situations like shortages of medicines during pandemics.
– India, South Korea, Japan, the United States, and the European Union initiated an alliance on June 6, 2024, to create a flexible supply chain in the biopharmaceutical sector.
– This announcement was made during the inauguration meeting of the Biopharmaceutical Alliance held at the Bio International Convention 2024 in San Diego, California.
– Which is the world’s largest biopharmaceutical exhibition.
– Government officials from participating countries and representatives of biotech and pharmaceutical companies attended the meeting.
Note:
– The Biopharmaceutical Alliance was launched in response to experiences of drug shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic.
European Union:
– The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of 27 member countries primarily located in Europe.
– Its objective is to enhance cooperation among member countries, promote economic stability and prosperity, and ensure peace and security.
PDF Download: Click here


